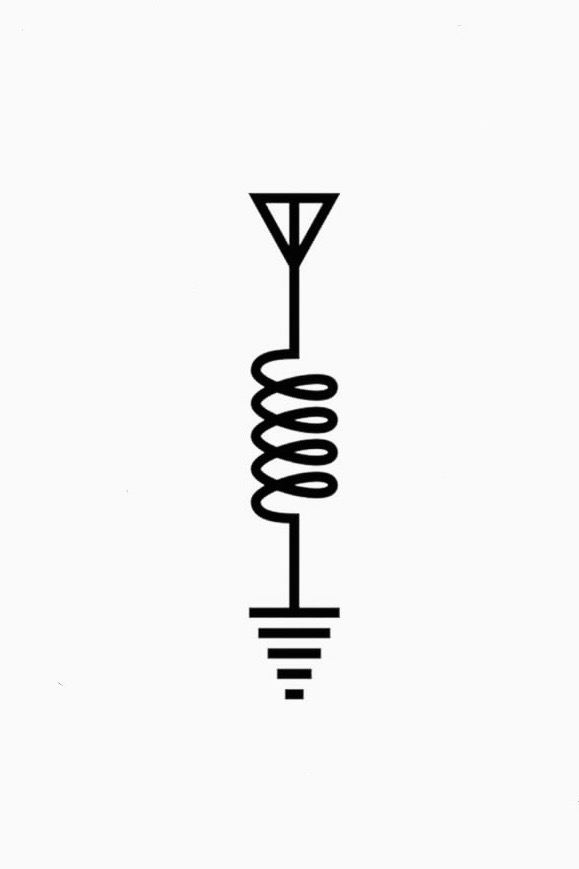

Great questions, one which highlights my own knowledge gap beyond knowing that for a given feedline and antenna combination, you’ll have some measure of impedance. At the most basic level, your radio will “see” some impedance value. In the amateur radio world this is generally 50Ω. If our antenna system (feedline + radiator) presents 450Ω (quite common), we use a 9:1 transformer to get it to match. This allows us to use our radio on that system without (1) stray current returning to the radio and damage our transmission circuits, and (2) at full power but with inherent loss of signal owing to antenna inefficiency.
Case in point, I have a commercially-purchased multi-band EFHW antenna which presents varying amounts of impedance to the radio. This system includes a transformer (I think it’s 9:1) so that on the bands of interest, there’s a resistance match and as a result an SWR that’s suitable to make decent transmissions on.
As a tangential example, J-pole antennas have a built-in matching system which uses no special parts. It’s composed of a matching section and radiator. The combination of matching section, radiator length, and physical feedpoint allow this type of antenna to sort of self-manage impedance.
The difference here is that a j-pole is a monoband antenna, and a long wire with transformer can often be functional on many bands, depending on length, where the lowest useable frequency is the inverse of its length.








There is certainly a lot to learn, and you would benefit greatly from joining the hobby officially. If you are US-based, you can take the amateur radio exam after memorizing the answers for the exam (a legal and encouraged practice), the exam itself can be administered remotely via Zoom.
I am beyond my technical knowledge if I tried to explain why we use transformers to get an impedance match; I only know what we do.