TLDR: Google’s DeepMind has developed a new open sourced AI system called AlphaProteo, which can design novel proteins that bind to target molecules. This technology has the potential to accelerate progress in various fields, including drug development, disease understanding, and diagnosis.
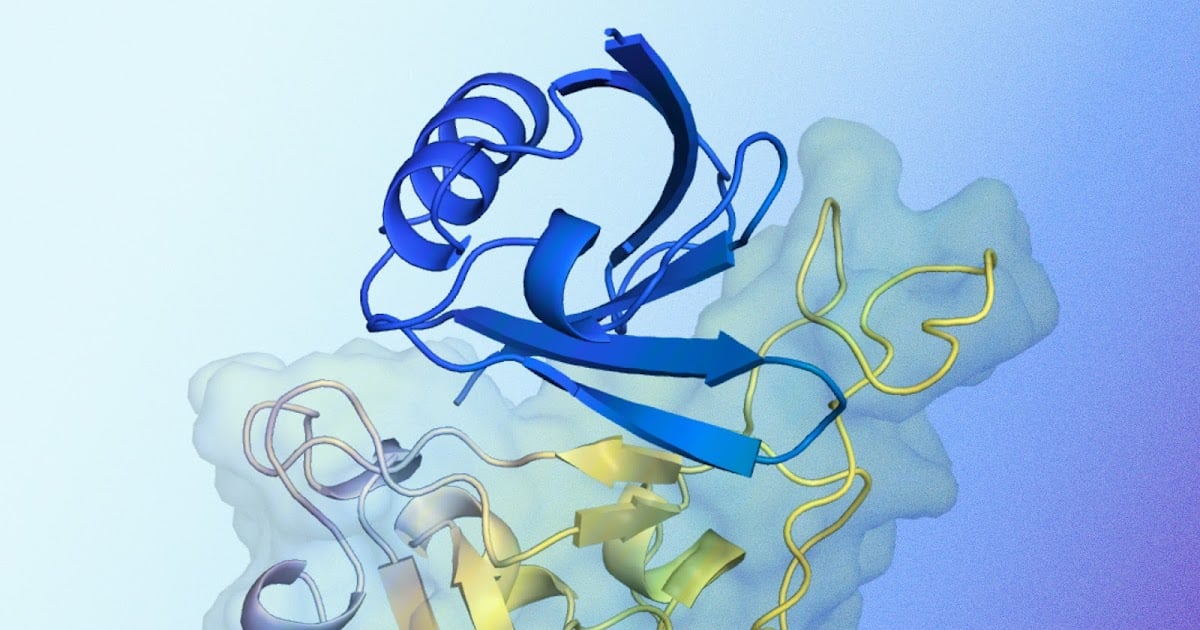
AlphaProteo was trained on vast amounts of protein data and has learned the intricate ways molecules bind to each other. It can generate candidate proteins that bind to target molecules at specific locations, and its designs have been validated through experiments.
The system has shown promising results, achieving higher experimental success rates and better binding affinities than existing methods. It has also been able to design successful protein binders for challenging targets, such as VEGF-A, which is associated with cancer and complications from diabetes.
However, the system is not perfect and has limitations, such as being unable to design successful binders against certain targets. To address these limitations, DeepMind is working to improve and expand AlphaProteo’s capabilities.
The development of AlphaProteo raises important questions about responsible development and biosecurity. DeepMind is working with external experts to develop best practices and is committed to sharing its work in a phased approach.
Overall, AlphaProteo has the potential to revolutionize protein design and accelerate progress in various fields, but it requires careful consideration of its limitations and potential risks.